Introduction
Kafka and RabbitMQ – These two terms are frequently thrown around in tech meetings discussing distributed architecture. I have been part of a series of such meetings where we discussed their pros and cons, and whether they fit our needs or not. Here’s me documenting my findings for others and my future self.
Message Routing
With respect to message routing capabilities, Kafka is very light. Producers produce messages to topics. Topics can further have partitions (like sharding). Kafka logs the messages in its very simple data structure which resembles… a log! It can scale as much as the disk can.
Consumers connect to these partitions to read the messages. Kafka uses a pull-based approach, so the onus of fetching messages and tracking offsets of read messages lies on consumers.
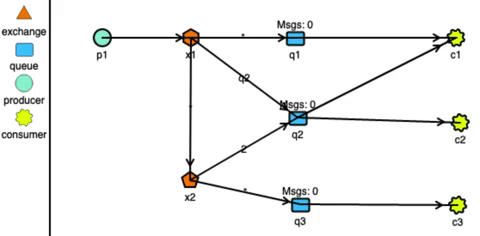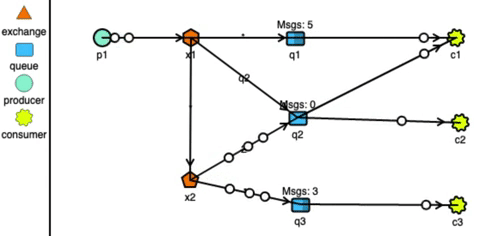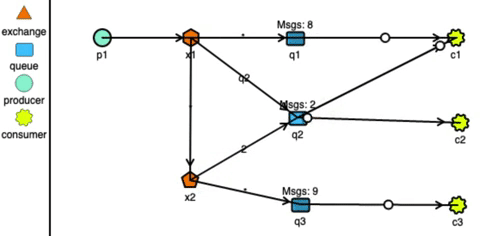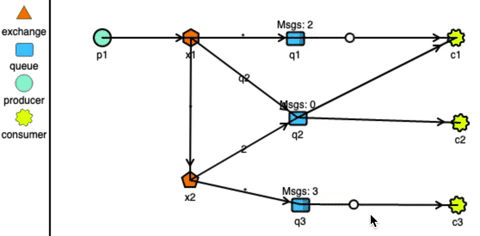
RabbitMQ has very strong routing capabilities. It can route the messages through a complex system of exchanges and queues. Producers send messages to exchanges which act according to their configurations. For example, they can broadcast the message to every queue connected with them, or deliver the message to some selected queues, or even expire the messages if not read in a stipulated time.
Exchanges can also pass messages to other exchanges, making a wide variety of permutations possible. Consumers can listen to messages in a queue or a pattern of queues. Unlike Kafka, RabbitMQ pushes the messages to the consumers, so the consumers don’t need to keep track of what they have read.
Delivery Guarantee
Distributed systems can have 3 delivery semantics:
at-most-once delivery
In case of failure in message delivery, no retry is done which means data loss can happen, but data duplication can not. This isn’t the most used semantic due to obvious reasons.
at-least-once delivery
In case of failure in message delivery, retries are done untill delivery is successfully acknowledged. This ensures no data is lost but this can result in duplicated delivery.
exactly-once delivery
Messages are ensured to be delivered exactly once. This is the most desirable delivery semantic and almost impossible to achieve in a distributed enviornment.
Both Kafka and RabbitMQ offer at-most-once and at-least-once delivery guarantees.
Kafka provides exactly-once delivery between producer to the broker using idempotent producers (enable.idempotence=true). Exactly-once message delivery to the consumers is more complex. It is achieved at consumers end by using transactions API and only reading messages belonging to committed transactions (isolation.level=read_committed).
To truly achieve this, consumers would need to avoid non-idempotent processing of messages in case a transaction has to be aborted, which is not always possible. So, Kafka transactions are not very useful in my opinion.
In RabbitMQ, exactly-once delivery is not supported due to the combination of complex routing and the push-based delivery. Generally, it’s recommended to use at-least-once delivery with idempotent consumers.
NOTE: Kafka Streams is an example of truely idempotent system, which it achieves by eliminating non-idempotent operations in a transaction. It, however is out of the scope of this article. I recommend reading “Enabling Exactly-Once in Kafka Streams” by Confluent if you want to dig in it further.
Throughput
Throughput of message queues depends on many variables like message size, number of nodes, replication configuration, delivery guarantees, etc. I will be focussing on the speed of messages produced versus consumed. The two cases which arise are:
- Queue is empty due to messages being consumed as and when they are produced.
- Queue is backed up due to consumers being offline or producers being faster than consumers.
RabbitMQ stores the messages in DRAM for consumption. In the case where consumers are not far behind, the messages are served quickly from the DRAM. Performance takes a hit when a lot of messages are unread and the queue is backed up. In this case, the messages are pushed to disk and reading from it is slower. So, RabbitMQ works faster with empty queues.
Kafka uses sequential disk I/O to read chunks of the log in an orderly fashion. Performance improves further in case fresh messages are being consumed, as the messages are served from the OS page cache without any I/O reads. However, it should be noted that implementing transactions as discussed in last section will have negative effect on the throughput.
Overall, Kafka can process millions of messages in a second and is faster than RabbitMQ. Whereas, RabbitMQ can process upwards of 20k messages per second.
Persistence
Persistence of messages is another front where both of these tools can not be more different.
Kafka is designed with persistent (or retention as they call it) in mind. A Kafka system can be configured to retain messages – both delivered and undelivered, by configuring either log.retention.hours or log.retention.bytes.
Retaining messages doesn’t effect the performance of Kafka. The consumers can replay retained messages by changing the offset of messages they have read.
RabbitMQ on the other hand, works very differently. Messages when delivered to multiple queues, are duplicated in these queues. These copies are then governed independently of each other by the policy of the queues they are in, and the exchanges they are passing. So to persist the messages in RabbitMQ:
- queues and exchanges need to be made durable,
- messages produced need to be tagged as persistent by the producer
Not to mention, this will have performance impact since disk is involved in an otherwise memory operation.
Conclusion
RabbitMQ offers complex routing use-cases which can not be realized with Kafka’s simple architecture. However, Kafka provides higher throughput and persistence of messages.


Very informative
ReplyDeleteNicely explained
ReplyDelete